Using Libraries
Course Home | What are packages? | Package Example
Node manages libraries through a tool called Node Package Manager or NPM for short.
NPM manages the installation of libraries, run your projects and contains details on your project. This is all controlled via a file in your project called package.json that will look something like this:
{
"name": "node-basics",
"version": "0.0.1",
"description": "A demonstration of npm init",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "mocha test"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/mwinteringham/free-node-basics-course.git"
},
"keywords": [
"Node",
"Training"
],
"author": "Mark Winteringham",
"license": "MIT",
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/mwinteringham/free-node-basics-course/issues"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/mwinteringham/free-node-basics-course#readme",
"dependencies": {
"selenium-webdriver": "^3.6.0"
}
}
As we can see the package.json contains:
- Details on the project in the form of the name, version, description and more
- Scripts that can be run to trigger off activities such as running tests or starting the app
- A list of libraries under the name dependencies that NPM can install
Creating your own package.json
To create your own package.json you can use NPM’s wizard to generate your file. By running npm init you will be presented with a walkthrough wizard that will guide you through creating a package.json. Similar to this example:
npm init
This utility will walk you through creating a package.json file.
It only covers the most common items, and tries to guess sensible defaults.
See `npm help json` for definitive documentation on these fields
and exactly what they do.
Use `npm install <pkg> --save` afterwards to install a package and
save it as a dependency in the package.json file.
Press ^C at any time to quit.
name: (free-node-basics-course) node-basics
version: (1.0.0) 0.0.1
description: A demonstration of npm init
entry point: (index.js) app.js
test command: mocha test
git repository: (https://github.com/mwinteringham/free-node-basics-course.git)
keywords: Node, Training
author: Mark Winteringham
license: (ISC) MIT
About to write to /Users/mark/Documents/Testing_Community/free-node-basics-course/package.json:
{
"name": "node-basics",
"version": "0.0.1",
"description": "A demonstration of npm init",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "mocha test"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/mwinteringham/free-node-basics-course.git"
},
"keywords": [
"Node",
"Training"
],
"author": "Mark Winteringham",
"license": "MIT",
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/mwinteringham/free-node-basics-course/issues"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/mwinteringham/free-node-basics-course#readme"
}
Is this ok? (yes) yes
Once your package.json is created you can then install and add in your required libraries. To add a new library to our project we first have to find the library we need. I find all the libraries I need on the Node Package Manager library. This is a remote repository where people can upload their Java libraries to, so others can benefit from them.
So for example, if we visit the site and search for ‘selenium-webdriver’, you should see the first result as follows
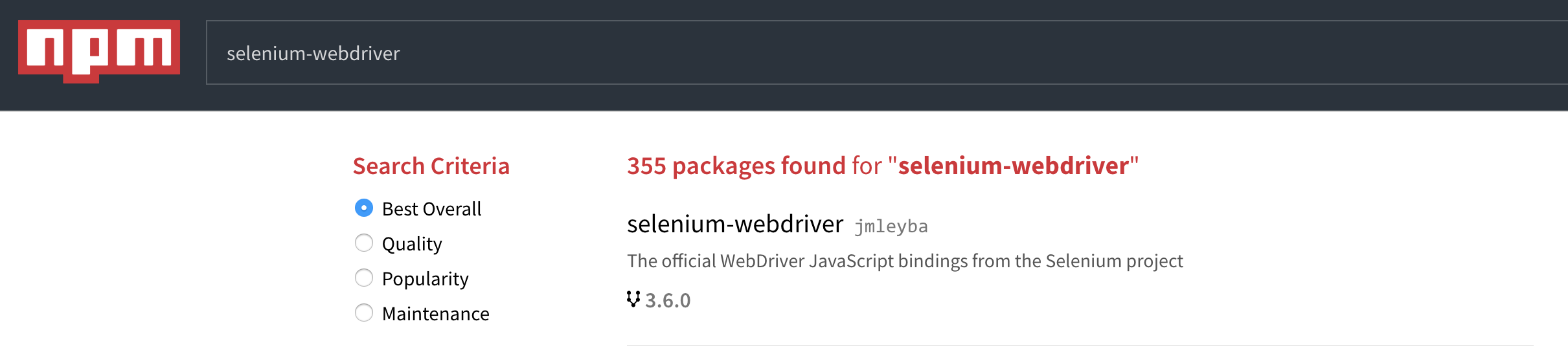
If we click on the first result for more details we will get more details on the library along with details in the top right hand corner:
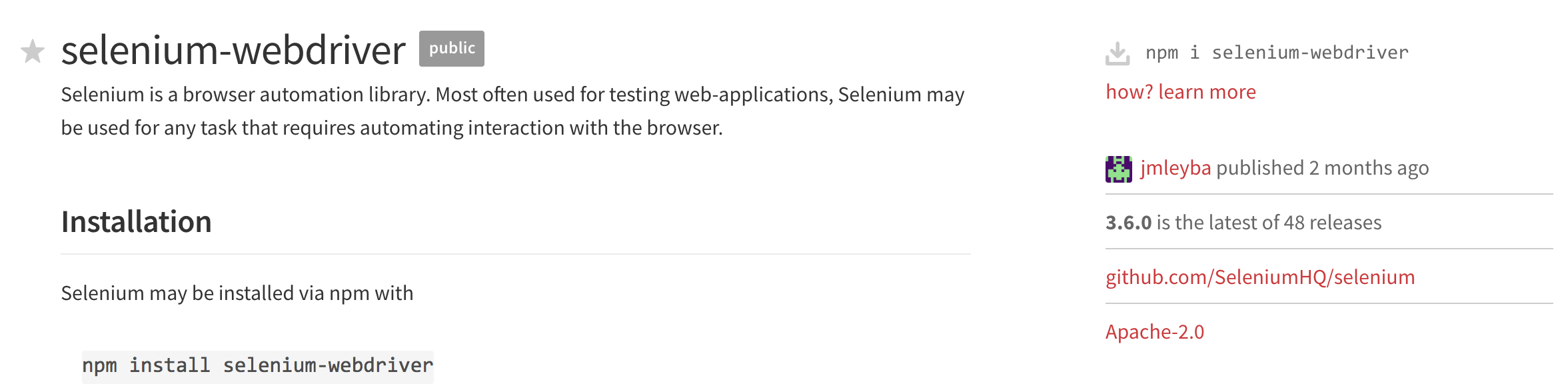
However, to ensure that the library is added to package.json we should run npm install selenium-webdriver --save. This will install the library and also added it to package.json for future reference.
Once installed, take a look at your project folder. You will notice a node_modules folder will have been created and the library (and it’s dependencies) will exist in the folder. This folder is local to your project and is used by your project to access the libraries you require to run your code.
Working with other projects
If you are working with a pre-existing project then you can run npm install and this will use the package.json to install all necessary libraries for the project


Comments